White Dwarfs & Planetary Nebulas
Two Stars, Three Dimensions, and Oodles of Energy
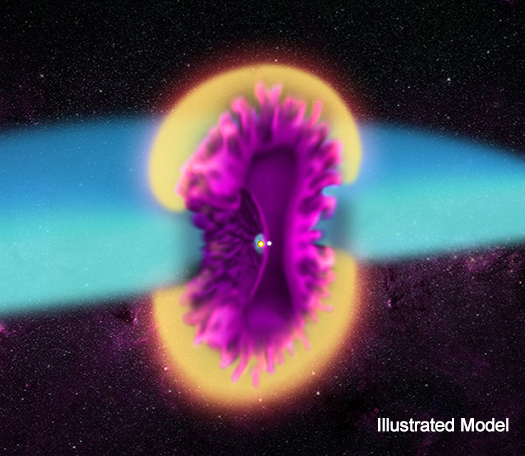
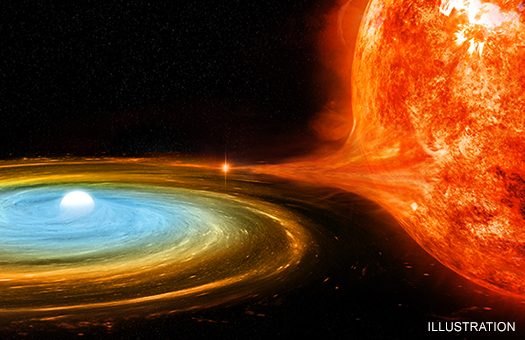
For decades, astronomers have known about irregular outbursts from the double star system V745 Sco, which is located about 25,000 light years from Earth. Astronomers were caught by surprise when previous outbursts from this system were seen in 1937 and 1989. When the system erupted on February 6, 2014, however, scientists were ready to observe the event with a suite of telescopes including NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory.
V745 Sco is a binary star system that consists of a red giant star and a white dwarf locked together by gravity. These two stellar objects orbit so closely around one another that the outer layers of the red giant are pulled away by the intense gravitational force of the white dwarf. This material gradually falls onto the surface of the white dwarf. Over time, enough material may accumulate on the white dwarf to trigger a colossal thermonuclear explosion, causing a dramatic brightening of the binary called a nova. Astronomers saw V745 Sco fade by a factor of a thousand in optical light over the course of about 9 days.
Watching a Volatile Stellar Relationship
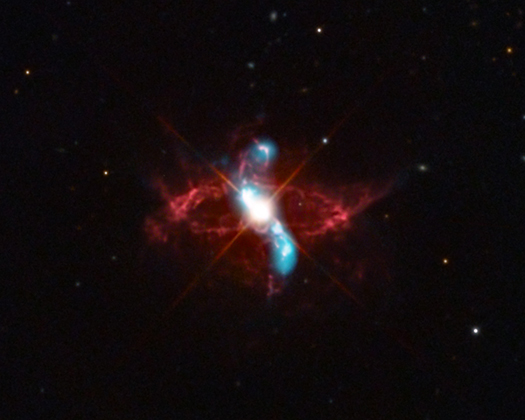
In biology, "symbiosis" refers to two organisms that live close to and interact with one another. Astronomers have long studied a class of stars – called symbiotic stars – that co-exist in a similar way. Using data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and other telescopes, astronomers are gaining a better understanding of how volatile this close stellar relationship can be.
R Aquarii (R Aqr, for short) is one of the best known of the symbiotic stars. Located at a distance of about 710 light years from Earth, its changes in brightness were first noticed with the naked eye almost a thousand years ago. Since then, astronomers have studied this object and determined that R Aqr is not one star, but two: a small, dense white dwarf and a cool red, giant star.
"Mini Supernova" Explosion Could Have Big Impact
In Hollywood blockbusters, explosions are often among the stars of the show. In space, explosions of actual stars are a focus for scientists who hope to better understand their births, lives, and deaths and how they interact with their surroundings.
Using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory, astronomers have studied one particular explosion that may provide clues to the dynamics of other, much larger stellar eruptions.
Doubling Down With Rare White Dwarf Systems
In the middle of the twentieth century, an unusual star was spotted in the constellation of Canes Venatici (Latin for "hunting dogs"). Years later, astronomers determined that this object, dubbed AM Canum Venaticorum (or, AM CVn, for short), was, in fact, two stars. These stars revolve around each other every 18 minutes, and are predicted to generate gravitational waves - ripples in space-time predicted by Einstein.
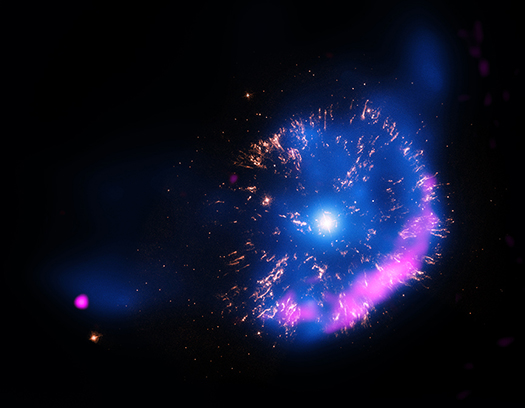
X-rays from a Reborn Planetary Nebula
These images of the planetary nebula Abell 30, (a.k.a. A30), show one of the clearest views ever obtained of a special phase of evolution for these objects. The inset image on the right is a close-up view of A30 showing X-ray data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory in purple and Hubble Space Telescope (HST) data showing optical emission from oxygen ions in orange. On the left is a larger view showing optical and X-ray data from the Kitt Peak National Observatory and ESA's XMM-Newton, respectively. In this image the optical data show emission from oxygen (orange) and hydrogen (green and blue), and X-ray emission is colored purple.
A planetary nebula - so called because it looks like a planet when viewed with a small telescope - is formed in the late stage of the evolution of a sun-like star.
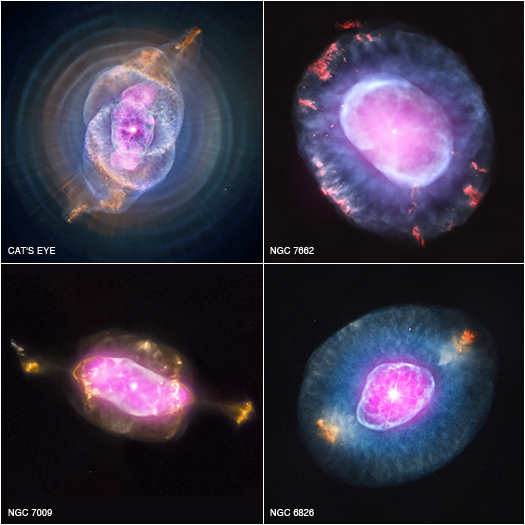
A Planetary Nebula Gallery
This gallery shows four planetary nebulas from the first systematic survey of such objects in the solar neighborhood made with NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. The planetary nebulas shown here are NGC 6543, also known as the Cat's Eye, NGC 7662, NGC 7009 and NGC 6826. In each case, X-ray emission from Chandra is colored purple and optical emission from the Hubble Space Telescope is colored red, green and blue.