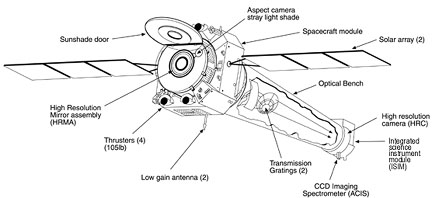
Chandra Specifications
An X-ray telescope is the only way astronomers can observe
the hot regions of the universe. The most powerful optical
telescopes, such as the Hubble Space Telescope, cannot see
the vast clouds of hot gas that stretch millions of light
years across and contain enough matter to make hundreds of
trillions of stars. X-ray telescopes allow us to image matter
swirling as close as 90 kilometers from the event horizon of
a stellar black hole or to track the expansion of a hot gas
bubble produced by an exploding star.
Chandra is the third of NASA's Great Observatories. The
mirrors on Chandra are the largest, most precisely shaped and
aligned, and smoothest mirrors ever constructed. The images
Chandra makes are twenty-five times sharper than the best
previous X-ray telescope. Chandra, which was launched by the
Space Shuttle on July 23, 1999, is helping scientists to
better understand the hot, turbulent regions of space and
answer fundamental questions about the origin, evolution, and
destiny of the universe.
Overall Specifications
|
|
Size (solar
arrays deployed):
|
13.8 m x 19.5 m (45.3 ft x 64.0 ft)
|
|
Weight:
|
4,800 kg (10,560 pounds)
|
|
Orbit:
|
10,000 km x 140,161 km (6,200 x 86,900 miles); 28.5
degree inclination
|
|
Ascending
node:
|
200 degrees
|
|
Argument of
perigee:
|
270 degrees
|
|
Life:
|
minimum 5 years
|
|
Chandra Specifications
|
|
Power:
|
two 3-panel silicon solar arrays (2350 W) three 40
amp-hour nickel hydrogen batteries
|
|
Antennas:
|
two low-gain, conical log spiral antennas
|
|
Frequencies:
|
transmit 2250 MHz, receive 2071.8 MHz
|
|
Command
Link:
|
2 kilobits per second (kbps)
|
|
Data
Recording:
|
solid state recorder; 1.8 gigabits (16.8 hours)
recording capability
|
|
Downlink
Operations:
|
downloaded typically every 8 hours
|
|
Contigency
Mode:
|
32 kbps
|
|
Safing:
|
autonomous operation
|
|
Telescope System
|
|
High Resolution
Mirror Assembly:
|
4 nested pairs of grazing incidence paraboloid and
hyperboloid mirrors
|
|
Length:
|
each 83.3 cm (32.8 in) long
|
|
Weight:
|
956.4 kg (2,104 pounds) total
|
|
Focal
Length:
|
10 meters (32.8 ft)
|
|
Outer
Diameter:
|
1.2 meters (3.9 ft)
|
|
Field of
View:
|
1.0 degree diameter
|
|
Ang.
Resolution:
|
0.5 arcsec
|
|
Altitude
Control:
|
6 reaction wheel control 2 inertial reference units
|
|
Aspect
Camera:
|
1.40 deg x 1.40 deg field-of-view
|
|
Pointing
Stability:
|
0.25 arcsec (RMS) radius over 95% of all 10 second
periods
|
|
Pointing
Accuracy:
|
30 arcsec 99% of viewing time
|
|
Remarks:
|
Mirrors have an effective area of 400 sq. cm. @1 keV;
600 A iridium coating
|
|
Science Instruments
|
|
Advanced
Charged Couple Imaging Spectrometer
(ACIS):
|
Ten CCD chips in 2 arrays provide imaging and
spectroscopy; imaging resolution is 0.5 arcsec over the
energy range 0.2 - 10 keV;
sensitivity: 4x10-15 ergs-cm-2
sec-1 in 10 5 s
|
|
High Resolution
Camera (HRC):
|
Uses large field-of-view mircro-channel plates to make
X-ray images: ang. resolution < 0.5 arcsec over
field-of-view 31x31 arc0min; time resolution: 16
micro-sec
sensitivity: 4x10-15 ergs-cm-2
sec -1 in 10 5 s
|
|
High Energy
Transmission Grating (HETG):
|
To be inserted into focused X-ray beam; provides
spectral resolution of 60-1000 over energy range 0.4 -
10 keV
|
|
Low Energy
Transmission Grating (LETG):
|
To be inserted into focused X-ray beam; provides
spectral resolution of 40-2000 over the energy range
0.09 - 3 keV
|
|