May 26, 2003
CXC Press Release: 03-04
Data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory have enabled astronomers to use a new way to determine if a young star is surrounded by a planet-forming disk like our early Sun. These results suggest that disks around young stars can evolve rapidly to form planets, or they can be disrupted by close encounters with other stars.
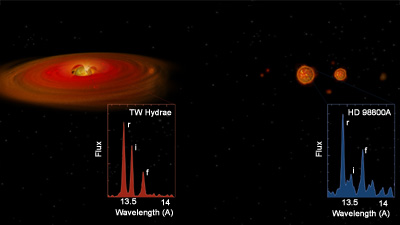
Chandra observed two young star systems, TW Hydrae and HD 98800, both of which are in the TW Hydrae Association, a loose cluster of 10 million-year-old stars. Observations at infrared and other wavelengths have shown that several stars in the TW Hydrae Association are surrounded by disks of dust and gas. At a distance of about 180 light years from Earth, these systems are among the nearest analogs to the early solar nebula from which Earth formed.
"X-rays give us an excellent new way to probe the disks around stars," said Joel Kastner of the Rochester Institute of Technology in Rochester, NY during a press conference today in Nashville, Tenn. at a meeting of the American Astronomical Society. "They can tell us whether a disk is very near to its parent star and dumping matter onto it, or whether such activity has ceased to be important. In the latter case, presumably the disk has been assimilated into larger bodies - perhaps planets--or disrupted."
Kastner and his colleagues found examples of each type of behavior in their study. One star, TW Hydrae, namesake of the TW Hydrae Association, exhibited features in its X-ray spectrum that provide strong, new evidence that matter is accreting onto the star from a circumstellar disk. They concluded that matter is guided by the star's magnetic field onto one or more hot spots on the surface of the star.
In contrast, Chandra observations of the young multiple star system HD 98800 revealed that its brightest star, HD 98800A, is producing X-rays much as the Sun does, from a hot upper atmosphere or corona. HD 98800 is a complex multiple-star system consisting of two pairs of stars, called HD 98800A and HD 98800B. These pairs, each of which is about an Earth-Sun distance apart, orbit each other at about the same distance as Pluto orbits the Sun.
"Our X-ray results are fully consistent with other observations that show that accretion of matter from a disk in HD 98800A has dropped to a low level," said Kastner. "So Chandra has thrown new weight behind the evidence that any disk in this system has been greatly diminished or destroyed in ten million years, perhaps by the ongoing formation of planets or by the companion stars."
The new X-ray technique for studying disks around stars relies on the ability of Chandra's spectrometers to measure the energies of individual X-rays very precisely. By comparing the number of X-rays emitted by hot gas at specific energies from ions such as oxygen and neon, the temperature and density of particles can be determined. This new technique will help astronomers to distinguish between an accretion disk and a stellar corona as the origin of intense X-ray emission from a young star.
Other members of the research team are David Huenemoerder, Norbert Schulz, and Claude Canizares from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and David Weintraub from Vanderbilt University. NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala., manages the Chandra program, and TRW, Inc., Redondo Beach, Calif., is the prime contractor for the spacecraft. The Smithsonian's Chandra X-ray Center controls science and flight operations from Cambridge, Mass., for the Office of Space Science at NASA Headquarters, Washington.
The image and additional information are available at:
MEDIA CONTACTS
Steve Roy
Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, AL
Phone: 256-544-6535
Megan Watzke
Chandra X-ray Observatory Center, CfA, Cambridge, MA
Phone: 617-496-7998