CXC Home | Search | Help | Image Use Policy | Latest Images | Privacy | Accessibility | Glossary | Q&A
1. Light Path
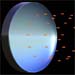
The Chandra Observatory is first oriented toward a cosmic X-ay source. View the animation.
(Illustration: NASA/CXC/D.Berry & A.Hobart)
The Chandra Observatory is first oriented toward a cosmic X-ay source. View the animation.
(Illustration: NASA/CXC/D.Berry & A.Hobart)
Download:
2. Light Path - Showing Mirrors, HRC
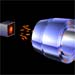
Next, X-ray photons entering the telescope are reflected at grazing angles and focused onto an electronic detector to make an image of a cosmic source. View the animation.
(Illustration: NASA/CXC/D.Berry & A.Hobart)
Next, X-ray photons entering the telescope are reflected at grazing angles and focused onto an electronic detector to make an image of a cosmic source. View the animation.
(Illustration: NASA/CXC/D.Berry & A.Hobart)
3. Light Path - Close-up of HRC
Here is a closeup showing the focusing of the X-rays onto an electronic detector. View the animation.
(Illustration: NASA/CXC/D.Berry & A.Hobart)
Here is a closeup showing the focusing of the X-rays onto an electronic detector. View the animation.
(Illustration: NASA/CXC/D.Berry & A.Hobart)
4. Mirror Comparison
X-rays that strike a mirror head-on are absorbed. View the animation.
(Illustration: NASA/CXC/D.Berry)
X-rays that strike a mirror head-on are absorbed. View the animation.
(Illustration: NASA/CXC/D.Berry)
Download:
5. Nested X-ray Mirrors
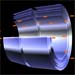
X-rays that hit a mirror at grazing angles are reflected like a pebble skipping across a pond. Thus, X-ray telescope mirrors are shaped like barrels rather than dishes. View the animation.
(Illustration: NASA/CXC/D.Berry)
X-rays that hit a mirror at grazing angles are reflected like a pebble skipping across a pond. Thus, X-ray telescope mirrors are shaped like barrels rather than dishes. View the animation.
(Illustration: NASA/CXC/D.Berry)
6. Focusing X-rays
Chandra's X-ray mirror assembly focuses X-rays onto a detector to produce an image. View the animation.
(Illustration: NASA/CXC/D.Berry)
Chandra's X-ray mirror assembly focuses X-rays onto a detector to produce an image. View the animation.
(Illustration: NASA/CXC/D.Berry)
Download:
7. Schematic of Grazing Incidence, X-Ray Mirror
This cutaway illustrates the design and functioning of the High Resolution Mirror Assembly (HRMA) on Chandra.
(Illustration: NASA/CXC/D.Berry)
This cutaway illustrates the design and functioning of the High Resolution Mirror Assembly (HRMA) on Chandra.
(Illustration: NASA/CXC/D.Berry)
8. Schematic of Grazing Incidence, X-Ray Telescope
This cross section through four nested pairs of mirrors illustrates the principle of grazing incidence reflection and focusing of X-rays. Two reflections are required to make an image. The grazing angles range from about 3.5 degrees for the outer pair to about 2 degrees for the inner pair.
(Illustration: NASA/CXC/S. Lee)
This cross section through four nested pairs of mirrors illustrates the principle of grazing incidence reflection and focusing of X-rays. Two reflections are required to make an image. The grazing angles range from about 3.5 degrees for the outer pair to about 2 degrees for the inner pair.
(Illustration: NASA/CXC/S. Lee)
Download: