General
Happy Birthday to Our Fellow 'Great Observatory'
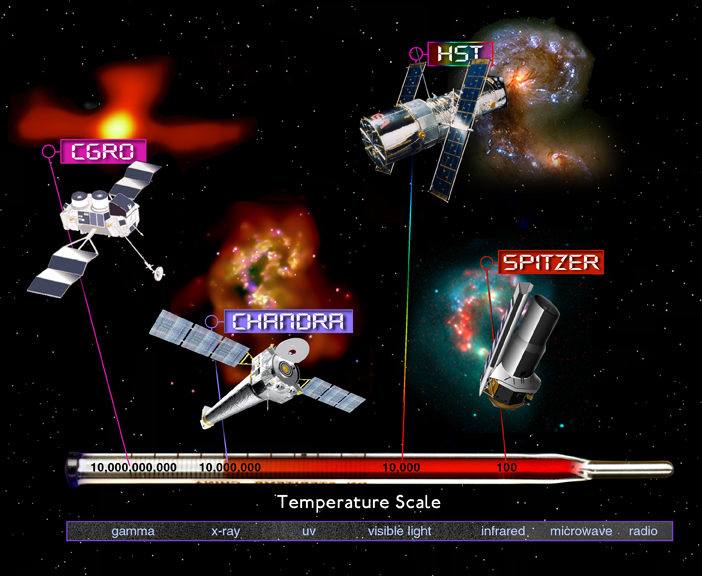
If you are at all interested in astronomy, chances are you’ve heard that the Hubble Space Telescope is celebrating its 25th anniversary this week. What some people may not know is that Hubble is one of four siblings, so to speak. Back in the 1980s, NASA commissioned the"Great Observatories," each designed and built to study different wavelengths of light.
The four Great Observatories, in order of their launches that took place between 1990 and 2003, are Hubble, the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory, the Chandra X-ray Observatory, and the Spitzer Space Telescope. You can learn a little more about each of these telescopes here: http://www.nasa.gov/audience/forstudents/postsecondary/features/F_NASA_…
Where Are They Now? Steve Hawley
Steve Hawley was the flight engineer on the STS-93 Columbia mission that carried Chandra into space in 1999. Before that he was on four previous shuttle flights, one in 1990 to deploy the Hubble Space Telescope, and one in 1997 to assist in making major upgrades and repairs to Hubble. His role in the deployment of two of the most productive telescopes ever has secured him an important place in the history of astronomy.
At a recent symposium celebrating 15 years of Chandra Science, Steve sat down over breakfast to talk about his illustrious career so far, and plans for the future.

Steve Hawley
When did you first think you wanted to be an astronaut?
SH: I wanted to be astronomer since I was very young. My grandfather taught physics at a small college in Kansas. He used to say, "In physics, you learn how to think." In astronomy you can learn how the universe works just by looking. And I was drawn to become an astronaut NASA, because NASA is a great organization because they try to do things that have never been done before.
Chandra Celebrates The International Year of Light
The year of 2015 has been declared the International Year of Light (IYL) by the United Nations. Organizations, institutions, and individuals involved in the science and applications of light will be joining together for this yearlong celebration to help spread the word about the wonders of light.
In many ways, astronomy uses the science of light. By building telescopes that can detect light in its many forms, from radio waves on one end of the "electromagnetic spectrum" to gamma rays on the other, scientists can get a better understanding of the processes at work in the Universe.
Harvey's Voyage

Dr. Harvey Tananbaum at the Smithsonian's Castle Library in May 2006. (Credit: Jim Moran)
Visualizing the X-ray Universe: Stories About Science
Telling a story about science can come in many different shapes, from an image of the area around a black hole, to a three-dimensional model of the remains of an exploded star, to something as simple as a tweet about a planet. Working for the Chandra X-ray Observatory, one of NASA's “Great Observatories” that studies extremely hot regions in space such as colliding galaxies and neutron stars, there is no shortage of data to tell stories about. Chandra orbits about 1/3 of the way to the Moon so it can take long exposures of cosmic objects. This year, Chandra marks its 15th anniversary of science operations out in the cold, dark and somewhat dangerous void of space.
Perhaps 50% of the job of “visualizing the X-ray Universe” is figuring out how we need to look at Chandra’s X-ray data and asking ourselves: what questions are this data trying to answer? what do experts see in this data? how will non-experts view and understand the data? The remaining 50% of the job is then what to do with that data, to make it both accessible and understandable.
Chandra and the Camelopardalids
Update (05.28.14): According to the team at the OCC, Chandra was unharmed during this new meteor shower. They report that passage through the stream was 'thankfully unremarkable.' According to all of their information, there was no evidence for any type of impact and it was 'smooth sailing.'
This week, sky watchers will be treated to a special event: a new meteor shower. Meteor showers occur when Earth, on its orbit around the Sun, passes through the debris left behind by a comet. There are some debris fields that Earth passes through every year and produce regular meteor showers that many people have heard of. These include the Leonids in November and the Perseids in July and August.
Chandra "Enthusiastically Endorsed" for Extension in Senior Review
Peter Edmonds is the Chandra Press Scientist and, in addition to his work on publicizing Chandra science, has been heavily involved with the Chandra's Senior Review proposal since 2008.
In science, "peer review" is used to describe a process that determines whether a research paper should be published in a journal. One or more experts review the paper and determine its fate: are the results and discussion reliable and do they meet the publication standards of the journal?
What Makes an Astronomical Image Beautiful?
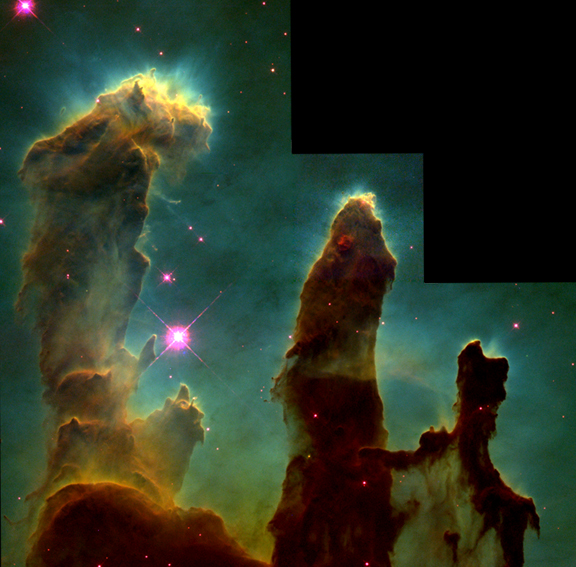
Astronomy is renowned for the beautiful images it produces. It's not hard to be impressed by an image like the Pillars of Creation or the Bullet Cluster, and the more eye-catching an image is, the bigger an audience it can potentially reach. So, as part of our job in astronomy outreach, we have each spent time thinking about what makes an astronomy image beautiful. As professionals, we’d like to go well beyond the intuition of the person who says, "I don't know anything about art, but I know what I like". One approach(1) is to list the key elements that make an image beautiful.
 |
 |
Two famous images, the Pillars of Creation from the Hubble Space Telescope on the left and the Bullet Cluster from the Chandra X-ray Observatory, Hubble and ground-based observatories on the right. Credit: left: NASA, ESA, STScI, J. Hester and P. Scowen (Arizona State University); right: X-ray: NASA/CXC/CfA/M.Markevitch et al.; Optical: NASA/STScI; Magellan/U.Arizona/D.Clowe et al.; Lensing Map: NASA/STScI; ESO WFI; Magellan/U.Arizona/D.Clowe et al.
Finding Patterns

Image: Frank Kovalchek, Wikimedia Commons
One of our favorite games to play with our kids is trying to find recognizable objects in clouds as they pass by on a sunny day. One cloud might look like an elephant, the next, a pirate ship.
Carnival of Space #328
Welcome to this week's Carnival of Space. It's been a busy Universe out there so let's jump right into it.
The Urban Astronomer has an excellent recap of Hubble's observations of a very unusual asteroid. This asteroid not only has a comet-like tail, it has six of them. Oh yeah, and they apparently change.
Over at the Smithsonian's Air & Space blog, they discuss a very provocative issue: if we go back to the Moon, where should we go and, maybe more importantly, where shouldn't we?
In advance of the recent Maven launch to Mars, the good folks over at Universe Today feature an excellent video that summarizes where the Curiosity rover has been and also where it will be heading in the future.

