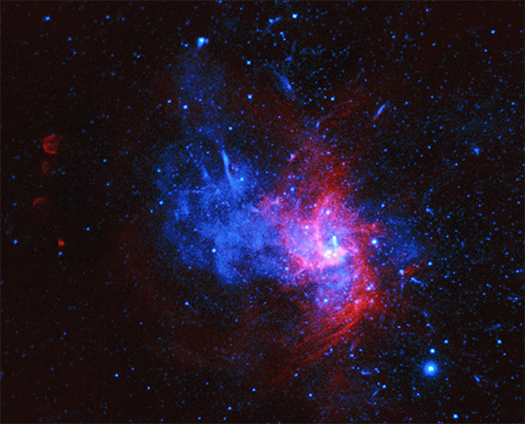
Data Sonification: Stellar, Galactic, and Black Hole
Your browser does not support the video tag.
This latest installment from our data sonification series features three diverse cosmic scenes. In each, astronomical data collected by NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and other telescopes are converted into sounds. Data sonification maps the data from these space-based telescopes into a form that users can hear instead of only see, embodying the data in a new form without changing the original content.
Upgrading Our Views of the Universe
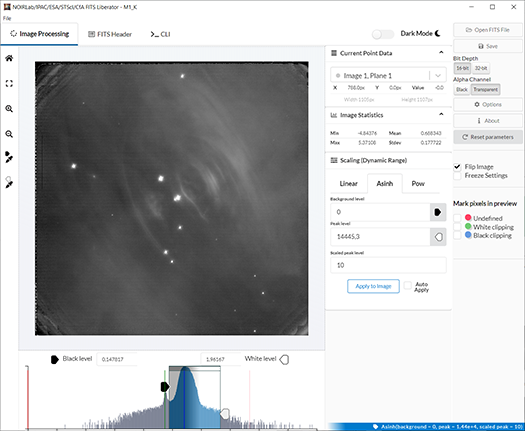
How do we image our Universe? There are many different ways of translating information from the cosmos. But in working with scientific data and image processing software, you can create your own astronomy images from FITS files. "FITS," which stands for Flexible Image Transport System, is a digital file format used mainly by astronomers to work with data of cosmic objects. Today, we are happy to help announce an update to the open source FITS Liberator software that can be used to process your own astronomical data. —Kimberly Kowal Arcand (CfA)
Astronomy is predominantly a visual science. However, an important tool is needed to produce breathtaking color images from the observations made with telescopes such as the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory, or the telescopes of NSF's NOIRLab at the international Gemini Observatory, Kitt Peak National Observatory, and Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory. The key to unlocking those magnificent vistas is specialized image-processing software.
Cosmic Poetry Competition 2021: The Winners
We are delighted to again welcome Jonathan Taylor as a guest blogger. Jonathan is the author of several novels and poetry collections, the editor of several anthologies, and Associate Professor in Creative Writing at the University of Leicester in the UK.
I've always been fascinated by the intersections and overlaps between Creative Writing and science. It's always seemed to me that poetry and cosmology, for example, share a great many characteristics, in their methods and means of communication: they both play with, even bend, language; they both use metaphor and analogy; they both re-enchant and defamiliarize our universe, so we see it anew. Having written various poems over the years for Chandra X-Ray Observatory (in March 2010, June 2010, April 2012, and August 2016), I often find the poetry is already there, waiting to be discovered, in the language used to capture Chandra's amazing revelations.
Hence, as part of their course, we encourage our Creative Writing students at Leicester University to explore some of the fascinating overlaps between their writing and scientific research – including the work of NASA and Chandra X-Ray Observatory. Over the years, this has resulted in various student competitions (in December 2010: part one and part two; May and June 2012: part one and part two; February 2016, and February 2017). In January 2021, we held a new competition for student writers, in which they were again invited to submit poems that explore – directly or indirectly, literally or metaphorically – the language and findings from one of Chandra's press releases. You can read the two beautiful winning entries below: 'IC 4593' by Laura Sygrove, and 'A New Cosmic Triad of Sound' by Rebecca Hughes.
From NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory to the Universe's Earliest Jet propulsion Laboratory
We are happy to welcome Thomas Connor as a guest blogger today. Thomas is a NASA Postdoctoral Fellow at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California and the author of a paper that is the subject of our most recent press release. He completed his undergraduate degree at Case Western Reserve University and earned his doctorate from Michigan State University. Prior to starting at JPL, Dr. Connor was a postdoctoral fellow at the Observatories of the Carnegie Institution for Science. His scientific interests include black holes in the dawn of the Universe, the evolution of galaxies in dense environments, and the structure of the Cosmic Web.
Most of the fundamental questions of astronomy relate to how the universe as we observe it was assembled. From stars and planets to nebulae and galaxies, many of the investigations of astronomy come down to crafting a coherent narrative of formation and evolution. Currently, that narrative is struggling to be built in the early universe, where supermassive black holes with masses a billion times that of the Sun are seen only a few hundred million years after the Big Bang. The challenge here is that, while we can model ways for such massive objects to form and grow, compressing that growth into such a short time scale is much more difficult. As an analogy, it is not surprising that an author can write a novel, but it would be astounding if she could do so in only one day.
Black holes grow by eating their surroundings, but, contrary to the typical depiction of these objects, they do not suck. Rather, they slowly nibble their way through an "accretion disk," an orbiting disk of gas that acts as a buffet for the black hole. As more gas makes its way inward, this disk will get hot from all of the friction of particles rubbing together, and it will start glowing like a hot coal. This bright light will act like a strong wind, pushing away further gas from replenishing the disk. Thus, the black hole's feeding is self-limiting — if it eats too fast, it won't be able to restock the buffet, and so it will have to slow down. This fundamental limit is why we are puzzled at how such massive black holes can exist so early.
On the Hunt for a Hidden Neutron Star

Emanuele Greco
We are pleased to welcome Emanuele Greco as a guest blogger. Emanuele is the first author of a paper describing the possible discovery of a neutron star left behind by supernova 1987A. Emanuele received a master’s degree in Physics at the University of Palermo in 2017. He is now completing his PhD in Astrophysics at the same University, where he is expected to defend his thesis next June. He spent six months of his PhD at the Anton Pannekoek Instituut of the University of Amsterdam. Emanuele’s main research interests deal with the X-ray spectroscopy of supernova remnants and objects embedded within their shells, with a particular focus on the different processes that generate X-ray emission.
Imagine having a bright and small light bulb and putting it behind a thick wall made of elements like iron and silicon. No light stemming from the bulb would be observed, because it is completely obscured by the wall. This quite simple scenario is perfectly suited also for the elusive compact object of supernova (SN) 1987A, which was investigated by scientists from University of Palermo (UniPa), INAF-Observatory of Palermo (OAPa), Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory (RIKEN) and University of Kyushu.
SN 1987A is the only naked-eye SN observed since telescopes were invented and offers a unique opportunity to watch a SN evolving into a supernova remnant (SNR) in this time of multi-wavelength and multi-messenger observatories simultaneously at work. This event was particularly important because neutrinos emitted from an exploding star were detected on Earth for the first time. This discovery implies that the core of the progenitor star must have collapsed producing a shock wave — similar to the sonic boom from a supersonic plane — that ejected part of the stellar material into the surrounding environment. As a result, a compact object such as a neutron star, a relic of the stellar core, should have formed in the very heart of SN 1987A. However, despite the continuous monitoring performed at almost all wavelengths since the SN was detected, no clear indication for this compact object has been found so far. Various hypotheses have been proposed to explain this non-detection, such as the formation of a black hole instead of a neutron star.
Rare Blast's Remains Discovered in Milky Way Center
Astronomers have found evidence for an unusual type of supernova near the center of the Milky Way galaxy, as reported in our latest press release. This composite image contains data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory (blue) and the NSF's Very Large Array (red) of the supernova remnant called Sagittarius A East, or Sgr A East for short. This object is located very close to the supermassive black hole in the Milky Way's center, and likely overruns the disk of material surrounding the black hole.
Researchers were able to use Chandra observations targeting the supermassive black hole and the region around it for a total of about 35 days to study Sgr A East and find the unusual pattern of elements in the X-ray signature, or spectrum. An ellipse on the annotated version of the images outlines the region of the remnant where the Chandra spectra were obtained.
Three's a Crowd: Triple Galaxy Collisions and Their Impact on Black Hole Accretion

Adi Foord
We are pleased to welcome Adi Foord as a guest blogger. Adi is the first author of a pair of papers that are the subject of the latest Chandra press release. She is a Post postdoctoral fellow at the Kavli Institute of Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology at Stanford University. She received her bachelor's degree in Physics & Astronomy from Boston University in 2014, and recently received her Ph.D. in Astronomy & Astrophysics from the University of Michigan (Summer 2020). Adi is a high-energy astrophysicist who is interested in how and which environmental properties impact supermassive black hole accretion and evolution. Most of her work uses X-ray observations of supermassive black holes, and she is currently focusing on systems where two supermassive black holes are in the process of merging.
With the advancement of gravitational wave detectors such as LIGO, we are starting to get real proof that black holes exist, and that some evolve over time via mergers with other black holes. The black holes that gravitational wave detectors like LIGO study are solar mass black holes. As the name and unit imply, these black holes have masses between about five and 100 times that of the sun, and are believed to be formed after the death of a massive star. But what about supermassive black holes, the massive counterparts to solar mass black holes that lie at the center of most massive galaxies? With the groundbreaking image supplied by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) in April 2019, we were given proof that supermassive black holes exist as well. But in order to have proof that they merge, and emit gravitational waves, we will have to wait for results from pulsar timing arrays (PTAs) and space-based interferometry (such as LISA). This is because the expected gravitational wave frequencies the supermassive black hole mergers are theorized to emit are outside the range of LIGO.
Chandra Studies Extraordinary Magnetar
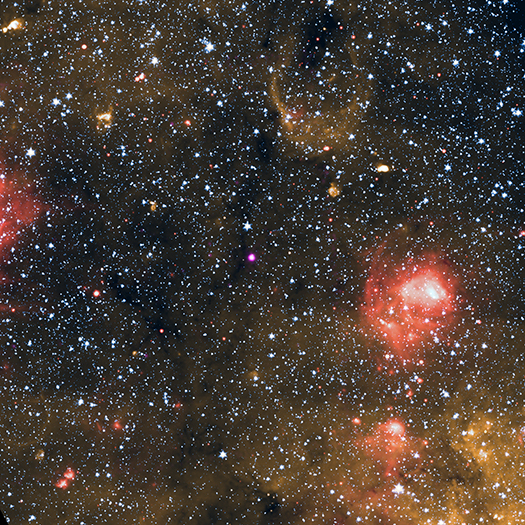

Magnetar J1818.0-1607
Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/Univ. of West Virginia/H. Blumer;
Infrared (Spitzer and Wise): NASA/JPL-CalTech/Spitzer
In 2020, astronomers added a new member to an exclusive family of exotic objects with the discovery of a magnetar. New observations from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory help support the idea that it is also a pulsar, meaning it emits regular pulses of light.
Magnetars are a type of neutron star, an incredibly dense object mainly made up of tightly packed neutrons, which forms from the collapsed core of a massive star during a supernova.
What sets magnetars apart from other neutron stars is that they also have the most powerful known magnetic fields in the Universe. For context, the strength of our planet's magnetic field has a value of about one Gauss, while a refrigerator magnet measures about 100 Gauss. Magnetars, on the other hand, have magnetic fields of about a million billion Gauss. If a magnetar was located a sixth of the way to the Moon (about 40,000 miles), it would wipe the data from all of the credit cards on Earth.
On the Hunt for a Missing Giant Black Hole
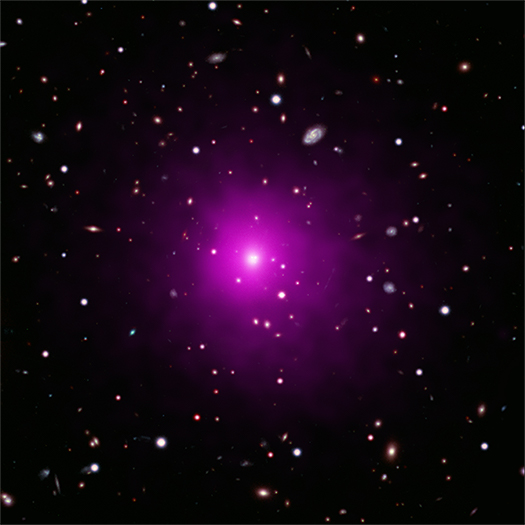

Abell 2261
Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/Univ of Michigan/K. Gültekin;
Optical: NASA/STScI and NAOJ/Subaru; Infrared: NSF/NOAO/KPNO
The mystery surrounding the whereabouts of a supermassive black hole has deepened.
Despite searching with NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have no evidence that a distant black hole estimated to weigh between 3 billion and 100 billion times the mass of the Sun is anywhere to be found.
This missing black hole should be in the enormous galaxy in the center of the galaxy cluster Abell 2261, which is located about 2.7 billion light years from Earth. This composite image of Abell 2261 contains optical data from Hubble and the Subaru Telescope showing galaxies in the cluster and in the background, and Chandra X-ray data showing hot gas (colored pink) pervading the cluster. The middle of the image shows the large elliptical galaxy in the center of the cluster.
Data Sonification: A New Cosmic Triad of Sound
Your browser does not support the video tag.
A new trio of examples of 'data sonification' from NASA missions provides a new method to enjoy an arrangement of cosmic objects. Data sonification translates information collected by various NASA missions — such as the Chandra X-ray Observatory, Hubble Space Telescope, and Spitzer Space Telescope — into sounds.
This image of the Bullet Cluster (officially known as 1E 0657-56) provided the first direct proof of dark matter, the mysterious unseen substance that makes up the vast majority of matter in the Universe. X-rays from Chandra (pink) show where the hot gas in two merging galaxy clusters has been wrenched away from dark matter, seen through a process known as "gravitational lensing" in data from Hubble (blue) and ground-based telescopes. In converting this into sound, the data pan left to right, and each layer of data was limited to a specific frequency range. Data showing dark matter are represented by the lowest frequencies, while X-rays are assigned to the highest frequencies. The galaxies in the image revealed by Hubble data, many of which are in the cluster, are in mid-range frequencies. Then, within each layer, the pitch is set to increase from the bottom of the image to the top so that objects towards the top produce higher tones.