Poetry Inspired by Chandra Discoveries
Science is a distinctly human endeavour that overlaps with many other fields.
Scientific discoveries can provide inspiration for music, art, literature and poetry. As an example of the latter, over several years we have hosted the results of poetry competitions run by Jonathan Taylor, a lecturer in Creative Writing at The University of Leicester in the UK. Jonathan asks students to write a poem based on one of the results in our press or image releases.
Blast from Black Hole in a Galaxy Far, Far Away
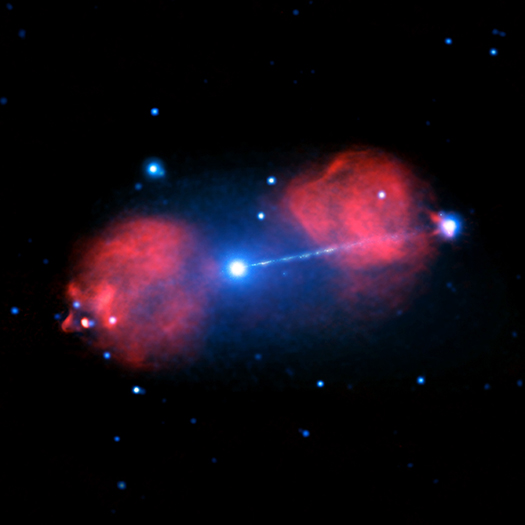
The Star Wars franchise has featured the fictitious "Death Star," which can shoot powerful beams of radiation across space. The Universe, however, produces phenomena that often surpass what science fiction can conjure.
The Pictor A galaxy is one such impressive object. This galaxy, located nearly 500 million light years from Earth, contains a supermassive black hole at its center. A huge amount of gravitational energy is released as material swirls towards the event horizon, the point of no return for infalling material. This energy produces an enormous beam, or jet, of particles traveling at nearly the speed of light into intergalactic space.
NASA's Chandra Finds Supermassive Black Hole Burping Nearby
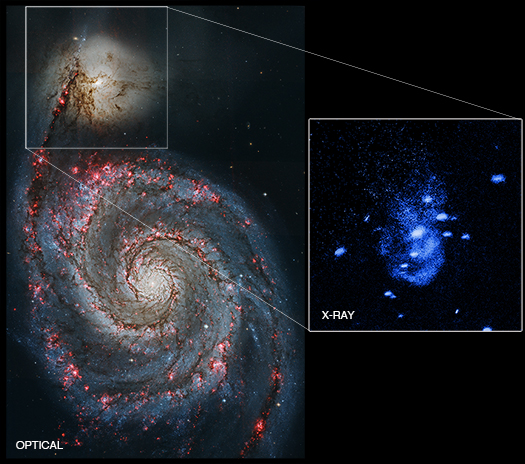
Astronomers have used NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory to discover one of the nearest supermassive black holes to Earth that is currently undergoing powerful outbursts, as described in our latest press release. This galactic burping was found in the Messier 51 galaxy, which is located about 26 million light years from Earth and, contains a large spiral galaxy NGC 5194 (also known by its nickname of the "Whirlpool"), merging with a smaller companion galaxy NGC 5195.
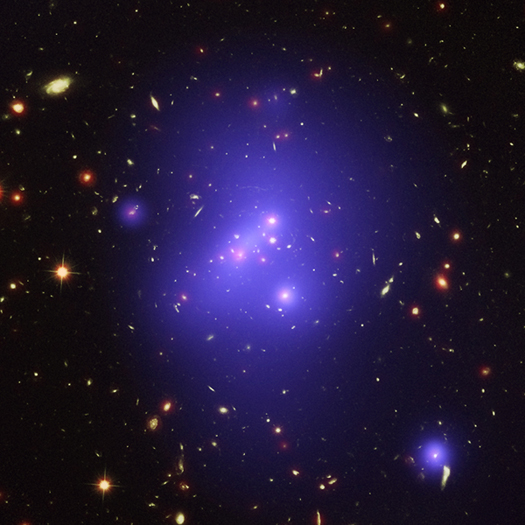
NASA's Great Observatories Weigh Massive Young Galaxy Cluster
Astronomers have made the most detailed study yet of an extremely massive young galaxy cluster using three of NASA's Great Observatories, as described in our latest press release [link to PR]. This multi-wavelength image shows this galaxy cluster, called IDCS J1426.5+3508 (IDCS J1426 for short), in X-rays from the Chandra X-ray Observatory in blue, visible light from the Hubble Space Telescope in green, and infrared light from the Spitzer Space Telescope in red.
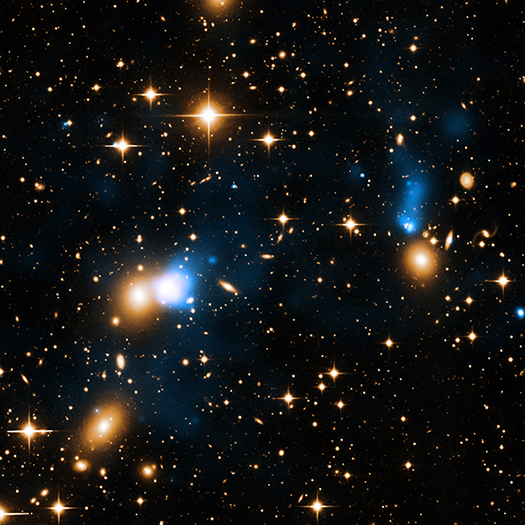
Chandra Finds Remarkable Galactic Ribbon Unfurled
An extraordinary ribbon of hot gas trailing behind a galaxy like a tail has been discovered using data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory, as described in our latest press release. This ribbon, or X-ray tail, is likely due to gas stripped from the galaxy as it moves through a vast cloud of hot intergalactic gas. With a length of at least 250,000 light years, it is likely the largest such tail ever detected. In this new composite image, X-rays from Chandra (blue) have been combined with data in visible light from the Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes (yellow) in the Canary Islands, Spain.
What Spawned the Jellyfish Nebula?
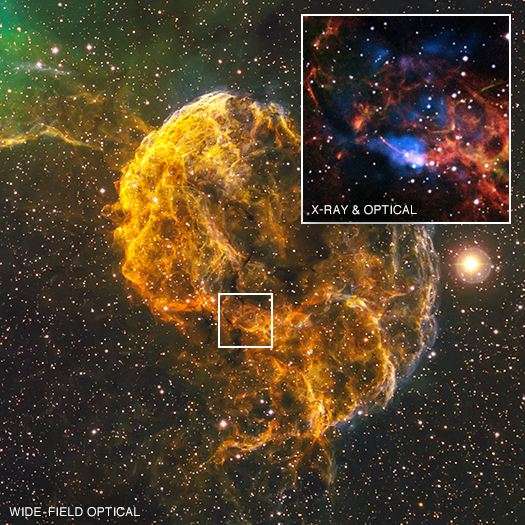
The Jellyfish Nebula, also known by its official name IC 443, is the remnant of a supernova lying 5,000 light years from Earth. New Chandra observations show that the explosion that created the Jellyfish Nebula may have also formed a peculiar object located on the southern edge of the remnant, called CXOU J061705.3+222127, or J0617 for short. The object is likely a rapidly spinning neutron star, or pulsar.
The Extraordinary Success of General Relativity
This month, people around the world are celebrating the hundredth anniversary of Albert Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity (GR). Although this theory can seem esoteric, it has an important practical application: the accuracy of Global Positioning System (GPS) relies on corrections from GR.
Where Alice in Wonderland Meets Albert Einestein
One hundred years ago this month, Albert Einstein published his theory of general relativity, one of the most important scientific achievements in the last century.
A key result of Einstein's theory is that matter warps space-time, and thus a massive object can cause an observable bending of light from a background object. The first success of the theory was the observation, during a solar eclipse, that light from a distant background star was deflected by the predicted amount as it passed near the Sun.
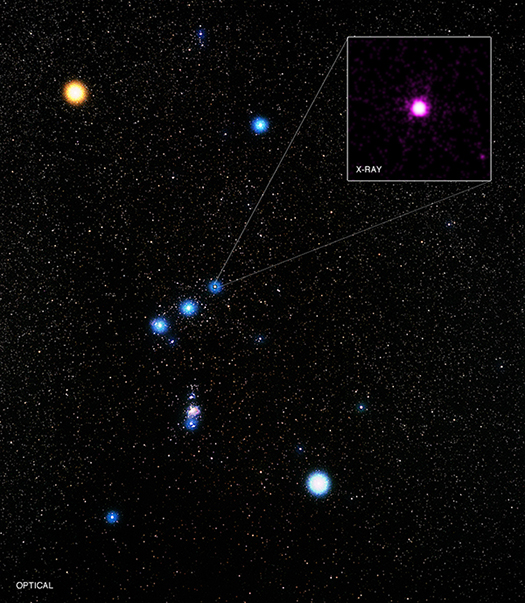
More Than Meets the Eye: Delta Orionis in Orion's Belt
One of the most recognizable constellations in the sky is Orion, the Hunter. Among Orion's best-known features is the "belt," consisting of three bright stars in a line, each of which can be seen without a telescope.
The westernmost star in Orion's belt is known officially as Delta Orionis. (Since it has been observed for centuries by sky-watchers around the world, it also goes by many other names in various cultures, like "Mintaka".) Modern astronomers know that Delta Orionis is not simply one single star, but rather it is a complex multiple star system.
Destroyed Star Rains onto Black Hole, Winds Blow it Back
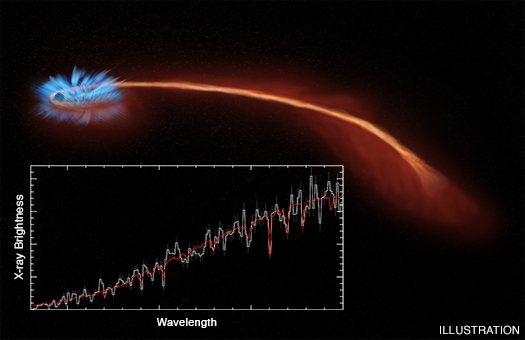
Astronomers have observed material being blown away from a black hole after it tore a star apart, as reported in our press release. This event, known as a "tidal disruption," is depicted in the artist's illustration.