CXC Home | Search | Help | Image Use Policy | Latest Images | Privacy | Accessibility | Glossary | Q&A
1
Accreting White Dwarf
This illustration depicts gas flowing from the large red, companion star into a disk and then onto the white dwarf that is hidden inside the white area. As the gas flows ever closer to the white dwarf, it gets increasingly hotter, as indicated by the change in colors from yellow to white. When a sufficient amount of gas has accumulated on the white dwarf star, it will undergo a thermonuclear explosion that will eject the outer layers of the star in a nova outburst.
(Credit: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss)
This illustration depicts gas flowing from the large red, companion star into a disk and then onto the white dwarf that is hidden inside the white area. As the gas flows ever closer to the white dwarf, it gets increasingly hotter, as indicated by the change in colors from yellow to white. When a sufficient amount of gas has accumulated on the white dwarf star, it will undergo a thermonuclear explosion that will eject the outer layers of the star in a nova outburst.
(Credit: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss)
2
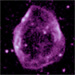
Chandra X-ray Image of DEM L71
Chandra's image of the supernova remnant DEM L71 reveals a hot inner cloud (aqua) of glowing iron and silicon surrounded by an outer blast wave. Data from the Chandra observation show that the central ten-million-degree Celsius cloud is the remains of a supernova explosion that destroyed a white dwarf star.
(Credit: NASA/CXC/Rutgers/J.Hughes et al.)
Chandra's image of the supernova remnant DEM L71 reveals a hot inner cloud (aqua) of glowing iron and silicon surrounded by an outer blast wave. Data from the Chandra observation show that the central ten-million-degree Celsius cloud is the remains of a supernova explosion that destroyed a white dwarf star.
(Credit: NASA/CXC/Rutgers/J.Hughes et al.)
3
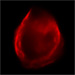
Optical (H-alpha) Image of DEM L71
This optical image of the supernova remnant DEM L71 taken February 18, 1998 with the CTIO 1.5 meter telescope also shows the outer blast wave. The bandwidth of the optical image is H-alpha (6567.90).
(Credit: Rutgers Fabry-Perot)
This optical image of the supernova remnant DEM L71 taken February 18, 1998 with the CTIO 1.5 meter telescope also shows the outer blast wave. The bandwidth of the optical image is H-alpha (6567.90).
(Credit: Rutgers Fabry-Perot)
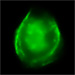
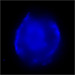
4
Chandra X-ray Images of DEM L71: Energy Cuts
(Credit: NASA/CXC/Rutgers/J.Hughes et al.)
(Credit: NASA/CXC/Rutgers/J.Hughes et al.)
Return to DEM L71 (12 Mar 03)