SNR 0519-69.0:
Cosmic Fireworks
 Credit: NASA/CXC/SAO
Credit: NASA/CXC/SAO
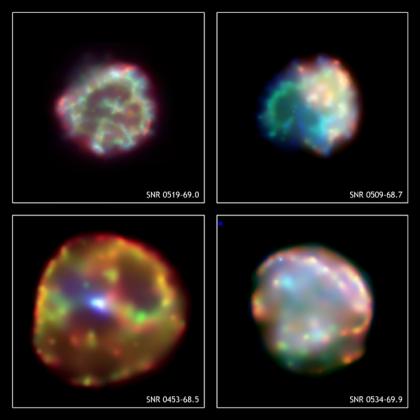
The remains of four supernovas in the nearby Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy provide a dazzling display of one of nature's most explosive events. These X-ray images show multimillion degree gas that has been heated by shock waves from the explosions. Moving in a clockwise direction from the upper left to the lower left, the approximate ages of the remnants are 600 years, 1500 years, 10,000 years and 13,000 years, respectively.
Chandra X-ray spectra provide important clues as to how these stars exploded. The remnants on the upper left, upper right and lower right show a concentration of elements typical of a Type Ia supernova. Such an explosion is triggered when matter is pulled from a companion star onto a white dwarf star and pushes it past the limit of stability. The ensuing thermonuclear explosion completely disrupts the white dwarf star.
In contrast, the supernova that produced the remnant SNR 0453-68.5 left behind a neutron star. This indicates that a Type II supernova occurred when the nuclear power source of a massive star became exhausted and the stellar core collapsed to form a neutron star, while the outer layers of the star were blown away. The rapidly spinning neutron star is ejecting a magnetized wind of extremely high-energy particles, which appears in the image as the elongated, bright blue-white spot at the center of the remnant.
| Fast Facts for SNR 0519-69.0: |
| Credit |
NASA/CXC/SAO |
| Scale |
Image is 1.85 arcmin per side. |
| Category |
Supernovas & Supernova Remnants |
| Coordinates (J2000) |
RA 05h 19m 34.90s | Dec -69º 02' 07.30" |
| Constellation |
Dorado
|
| Observation Dates |
2000-06-21 |
| Observation Time |
11 hours |
| Obs. IDs |
118
|
| Color Code |
Energy (Red: low energy; Green: medium energy; Blue: high energy) |
| Instrument |
ACIS |
| References | K. Borkowski et al 2006 Astrophys. J.642, L141 |
| Distance Estimate |
About 160,000 light years
|
| Release Date |
July 03, 2006 |
|
| Fast Facts for SNR 0509-68.7: |
| Credit |
NASA/CXC/SAO |
| Scale |
Image is 2.4 arcmin per side. |
| Category |
Supernovas & Supernova Remnants |
| Coordinates (J2000) |
RA 05h 09m 03.90s | Dec -68º 43' 19.00" |
| Constellation |
Dorado
|
| Observation Dates |
January 1-3, 2001 |
| Observation Time |
33 hours |
| Obs. IDs |
1045, 2410, 2416
|
| Color Code |
Energy (Red: low energy; Green: medium energy; Blue: high energy) |
| Instrument |
ACIS |
| Also Known As | N103B | | References | K. Borkowski et al 2006 Astrophys. J.642, L141 |
| Distance Estimate |
About 160,000 light years
|
| Release Date |
July 03, 2006 |
|
| Fast Facts for SNR 0453-68.5: |
| Credit |
NASA/CXC/SAO |
| Scale |
Image is 8.7 arcmin per side. |
| Category |
Supernovas & Supernova Remnants |
| Coordinates (J2000) |
RA 04h 53m 40.00s | Dec -68º 29' 45.00" |
| Constellation |
Dorado
|
| Observation Dates |
2001-12-18 |
| Observation Time |
11 hours |
| Obs. IDs |
1990
|
| Color Code |
Energy (Red: low energy; Green: medium energy; Blue: high energy) |
| Instrument |
ACIS |
| References | K. Borkowski et al 2006 Astrophys. J.642, L141 |
| Distance Estimate |
About 160,000 light years
|
| Release Date |
July 03, 2006 |
|
| Fast Facts for SNR 0534-69.9: |
| Credit |
NASA/CXC/SAO |
| Scale |
Image is 8.8 arcmin per side. |
| Category |
Supernovas & Supernova Remnants |
| Coordinates (J2000) |
RA 05h 34m 00.00s | Dec -69º 55' 00.00" |
| Constellation |
Dorado
|
| Observation Dates |
2001-09-01 |
| Observation Time |
17 hours |
| Obs. IDs |
1991
|
| Color Code |
Energy (Red: low energy; Green: medium energy; Blue: high energy) |
| Instrument |
ACIS |
| References | K. Borkowski et al 2006 Astrophys. J.642, L141 |
| Distance Estimate |
About 160,000 light years
|
| Release Date |
July 03, 2006 |
|
Visual Description:
Four images of different supernova remnants shown in the X-ray part of the electromagnetic spectrum are included in this image. Each image has a different color scheme showcasing bright blues, greens and oranges, and is labeled with its object name (from top left, SNR 0519-69.0, 0509-68.7, 0534-69.9, and 0453-68.5). Chandra's images of these supernova remnants show expanding shells of gas heated to millions of degrees by shock waves from supernova explosions. Moving in a clockwise direction from the upper left to the lower left, the approximate ages of the remnants are 600 years, 1,500 years, 10,000 years and 13,000 years, respectively. X-ray spectra indicate that the objects on the upper left, upper right and lower right are the remnants of Type Ia supernovas that completely disrupted a white dwarf star. In contrast, the remnant on the lower left was produced by a Type II supernova resulting from the gravitational collapse of a massive star. The explosion left behind a rapidly spinning neutron star that is ejecting a magnetized wind of extremely high-energy particles. This energetic wind appears in the image as the elongated, bright blue-white spot at the center of the remnant.