CXC Home | Search | Help | Image Use Policy | Latest Images | Privacy | Accessibility | Glossary | Q&A
1
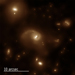
X-ray and Optical Images of CID-42
Evidence for a recoiling black hole has been found using data from Chandra, Hubble, XMM-Newton, and several ground-based telescopes. This black hole kickback was caused either by a slingshot effect produced in a triple black hole system, or from the effects of gravitational waves produced after two supermassive black holes merged a few million years earlier. Of the 2,600 X-ray sources found in this survey, only CID-42 coincides with two very close, compact optical sources. In these images, the two sources are seen in the HST data, but they are too close for Chandra to resolve separately.
(Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/SAO/F.Civano et al. Optical: NASA/STScI)
Evidence for a recoiling black hole has been found using data from Chandra, Hubble, XMM-Newton, and several ground-based telescopes. This black hole kickback was caused either by a slingshot effect produced in a triple black hole system, or from the effects of gravitational waves produced after two supermassive black holes merged a few million years earlier. Of the 2,600 X-ray sources found in this survey, only CID-42 coincides with two very close, compact optical sources. In these images, the two sources are seen in the HST data, but they are too close for Chandra to resolve separately.
(Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/SAO/F.Civano et al. Optical: NASA/STScI)
2
CID-42 with Scale Bar
(Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/SAO/F.Civano et al. Optical: NASA/STScI
(Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/SAO/F.Civano et al. Optical: NASA/STScI
Return to CID-42 (June 30, 2010)