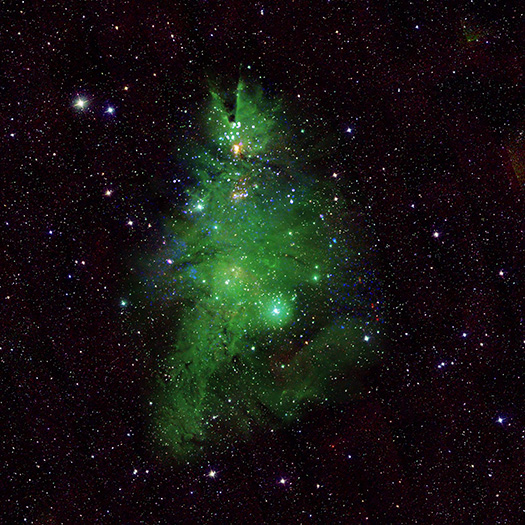
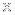This new image of NGC 2264, also known as the “Christmas Tree Cluster,” shows the shape of a cosmic tree with the glow of stellar lights. NGC 2264 is, in fact, a cluster of young stars — with ages between about one and five million years old — in our Milky Way about 2,500 light-years away from Earth. The stars in NGC 2264 are both smaller and larger than the Sun, ranging from some with less than a tenth the mass of the Sun to others containing about seven solar masses.
This new composite image enhances the resemblance to a Christmas tree through choices of color and rotation. The blue and white lights (which blink in the animated version of this image) are young stars that give off X-rays detected by NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory. Optical data from the National Science Foundation-supported WIYN 0.9-meter telescope on Kitt Peak shows a nebula of gas in the cluster in green, corresponding to the “pine needles” of the tree. Finally infrared data from the Two Micron All Sky Survey shows foreground and background stars in white. This image has been rotated clockwise by 160 degrees from the astronomer’s standard of North pointing upward, so that it appears like the top of the tree is toward the top of the image.

Young stars, like those in NGC 2264, are volatile and produce strong flares in X-rays and other types of variations seen at different wavelengths of light. The coordinated, blinking variations shown in this animation, however, are artificial, to emphasize the locations of the stars seen in X-rays and highlight the similarity of this object to a Christmas tree. In reality the variations of the stars are not synchronized.
The variations observed by Chandra and other telescopes are caused by several different processes. Some of these are related to activity involving magnetic fields, including flares like those undergone by the Sun — but much more powerful — and hot spots and dark regions on the surfaces of the stars that go in and out of view as the stars rotate. There can also be changes in the thickness of gas obscuring the stars, and changes in the amount of material still falling onto the stars from disks of surrounding gas.
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center manages the Chandra program. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory's Chandra X-ray Center controls science operations from Cambridge, Massachusetts, and flight operations from Burlington, Massachusetts.
This release features a composite image of a cluster of young stars looking decidedly like a cosmic Christmas tree! The cluster, known as NGC 2264, is in our Milky Way Galaxy, about 2,500 light-years from Earth. Some of the stars in the cluster are relatively small, and some are relatively large, ranging from one tenth to seven times the mass of our Sun.
In this composite image, the cluster's resemblance to a Christmas tree has been enhanced through image rotation and color choices. Optical data is represented by wispy green lines and shapes, which creates the boughs and needles of the tree shape. X-rays detected by Chandra are presented as blue and white lights and resemble glowing dots of light on the tree. Infrared data show foreground and background stars as gleaming specks of white against the blackness of space. The image has been rotated by 160 degrees from the astronomer's standard of North pointing upwards. This puts the peak of the roughly conical tree shape near the top of the image, though it doesn't address the slight bare patch in the tree's branches, at our lower right, which in a living room should probably be turned to the corner!
In this release, the festive cluster is presented as both a static image, and as a short animation. In the animation, blue and white X-ray dots from Chandra flicker and twinkle on the tree, like the lights on a Christmas tree.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||