Astronomers have discovered a black hole has torn apart a star (a phenomenon called a tidal disruption event, or TDE) in a surprising location, as described in this press release. This event occurred about 2,600 light-years away from the center of the black hole’s host galaxy, indicating the presence of a second large black hole. Most TDEs have been detected at the centers of galaxies where supermassive black holes are usually found.
A TDE happens when an infalling star is stretched or “spaghettified” by a black hole’s immense gravitational tidal forces. The shredded stellar remnants are pulled into a circular orbit around the black hole. This generates shocks and outflows with high temperatures that can be seen in ultraviolet and visible light. X-rays are produced when material from the destroyed star falls toward the black hole and is heated to millions of degrees.
The new TDE is called AT2024tvd and is in a galaxy some 600 million light-years from Earth. An optical survey by Caltech's Zwicky Transient Facility discovered AT2024tvd. To determine the location of the TDE, a team of researchers used data from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and Chandra X-ray Observatory and the NSF's Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array. The team estimates that the supermassive black hole responsible for the TDE has a mass of about a million Suns, compared to the black hole in the center of the galaxy that about 100 times more massive.
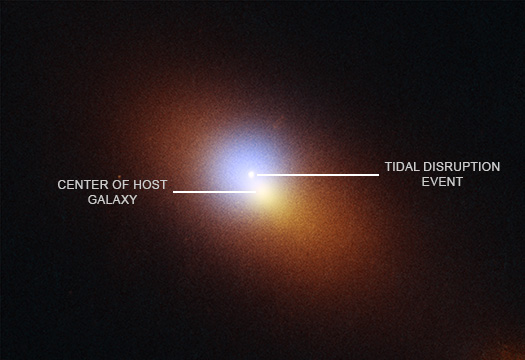
This composite image of the galaxy where AT2024tvd is found contains X-ray data from Chandra (blue), optical data from Hubble (orange), and ultraviolet data from Hubble (light blue). The center of the galaxy and the position of AT2024tvd, seen as the small, bright dot in the ultraviolet data, are labeled. The position of the Chandra source matches the position of the offset TDE. Chandra is the only X-ray telescope with vision sharp enough to distinguish between the offset TDE and the center of the galaxy.
Radio data from the VLA (not shown in this composite) also finds that AT2024tvd is located away from the center of the galaxy, in agreement with the Hubble and Chandra data.
How did the black hole get off-center? Previous theoretical studies have shown that black holes can be ejected out of the centers of galaxies because of three-body interactions, where a supermassive black hole encounters a pair of supermassive black holes, and the lowest-mass member gets kicked out. This may be the case here, given the stealthy black hole’s close proximity to the central black hole.
A paper with first author Yuhan Yao (University of California at Berkeley) describing these results appears in the latest issue of The Astrophysical Journal and is available at https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.17661.
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the Chandra program. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory's Chandra X-ray Center controls science operations from Cambridge, Massachusetts, and flight operations from Burlington, Massachusetts.
This release features a composite image of the tidal disruption event AT2024tvd and the galaxy in which it is found.
The galaxy is somewhat elliptical in shape and larger from side to side than from top to bottom, as though it has been slightly squished. The galaxy presents itself as a hazy orange glow, observed in optical and ultraviolet light, surrounding a hazy, off-centered circle of blue-colored X-ray light.
Near the center of the blue circle of X-rays is a small, bright dot in ultraviolet light. This dot is AT2024tvd, the location where a black hole has torn apart a star roughly 2,600 light-years away from the center of the black hole's host galaxy. Most tidal disruptions have been detected at the centers of galaxies where supermassive black holes are usually found. The presence of a tidal disruption this far away from the center of the galaxy indicates the presence of a second large black hole in the region.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share This |
|

