The 3D Printed Universe
Despite our limited abilities to travel to distant objects in outer space that can be thousands of light years away - if not millions or billions of light years away - astronomers, computer scientists, and other specialists are developing 3D models of the stars with data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, Hubble Space Telescope, Spitzer Space Telescope, and other telescopes. 3D modeling and printing objects in our Universe offers a unique tool to understand scientific data.
We offer two kinds of 3D printable objects in this section. The first is a set of specially-developed fully 3D models, and the second is a set of tactile plates that are developed as relief maps of images to help make the 2D data more experiential.
A binary star system of a red giant star and a white dwarf locked together by gravity. They orbit so closely that the outer layers of the red giant are pulled away by the gravitational force of the white dwarf.
(More information)
Download the Ejecta file
Download the Blast Wave file
Download the Ejecta and Blast Wave combined file
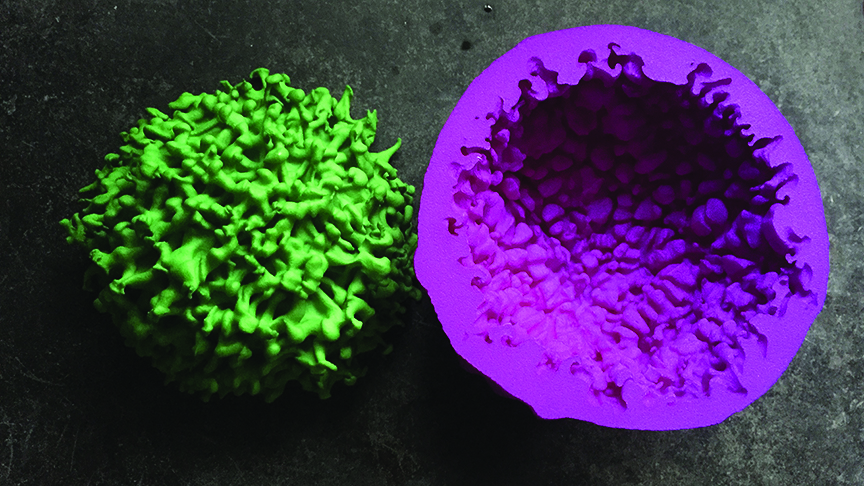
In 1987, astronomers noticed a new source of light in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a small satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. It was a spectacular explosion caused by the death of a massive star.
(More information)
Download the Ring Debris 2017 file
Download the Ring 2017 file
Download the Ring Debris and Ring combined file
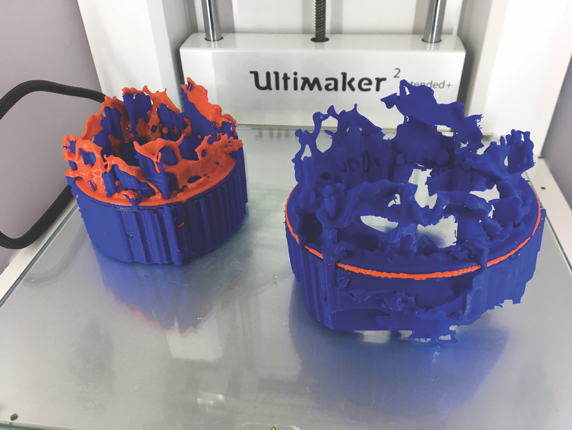

Over 400 years ago, in our own Milky Way galaxy, a star that was about 15 to 20 times the mass of our Sun detonated in a supernova explosion, giving us the Cassiopeia A remnant.
(More information)
Cas A Supernova Remnant Handout
Download the Cas A Supernova remnant with supports: 600k triangle OBJ, 27 MB
Download the volumetric data ASCII VTK files from telescope data: 3.94 MB
Download STL file commonly accepted by a wide range of 3D printers: 28.06 MB
Download the proprietary file format for Makerbot brand printers: 14.31 MB
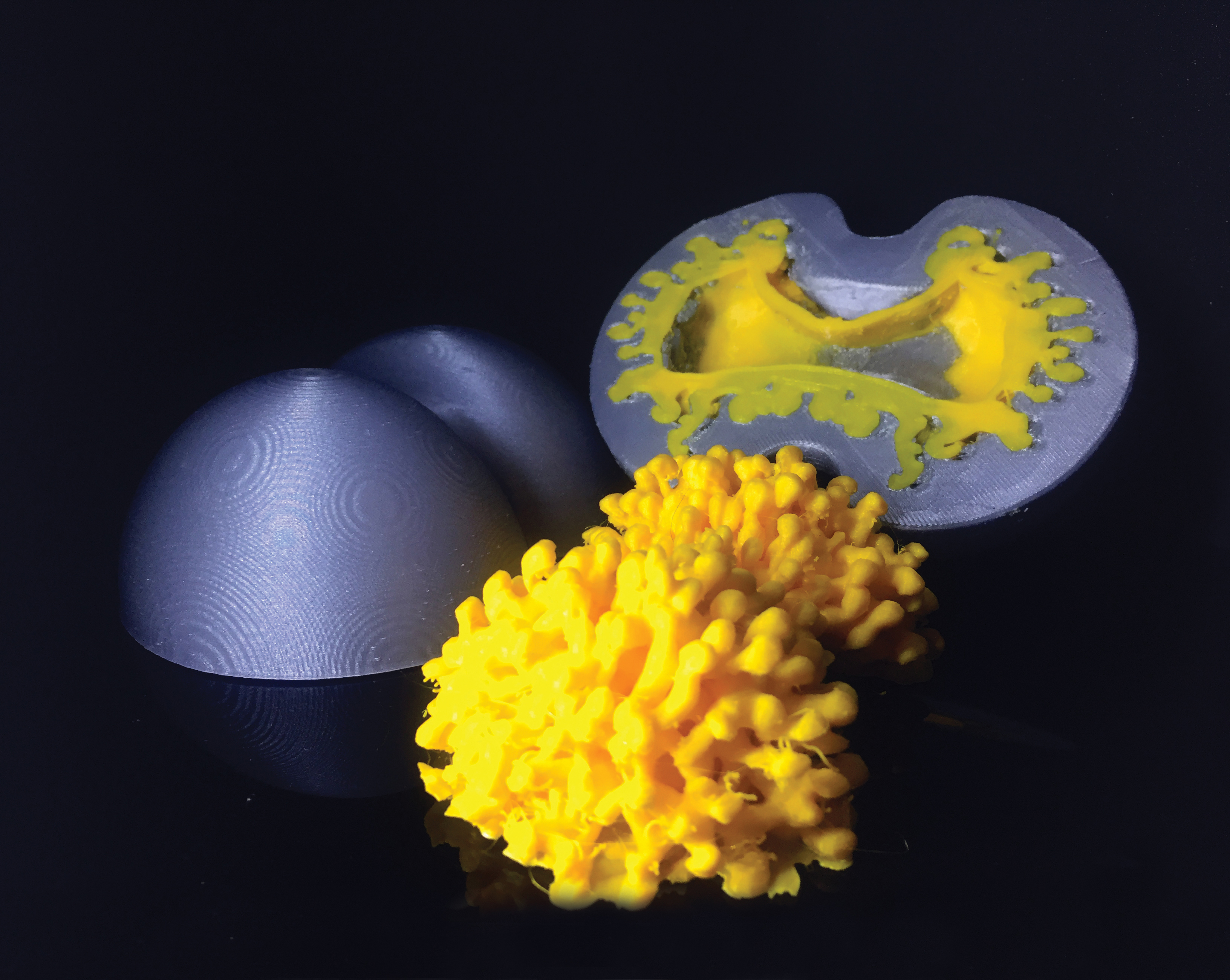
A Type Ia supernova, or when a white dwarf star pulls material from, or merges with, a nearby companion until a supernova explosion is triggered. The white dwarf is obliterated, sending its debris hurtling into space.
(More information)
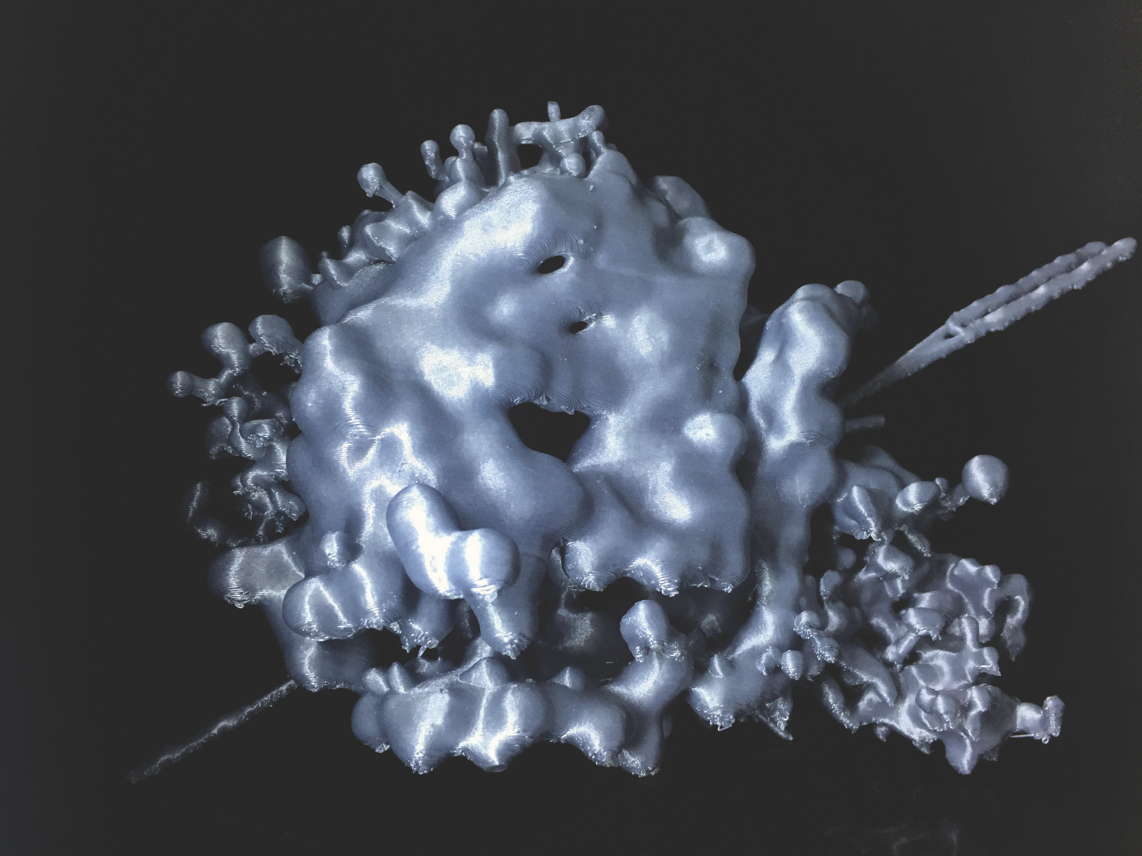
The Crab contains the remains of an exploded star with a pulsar (a rapidly spinning neutron star), at its core which is sending out bursts of radiation 30 times a second.
(More information)
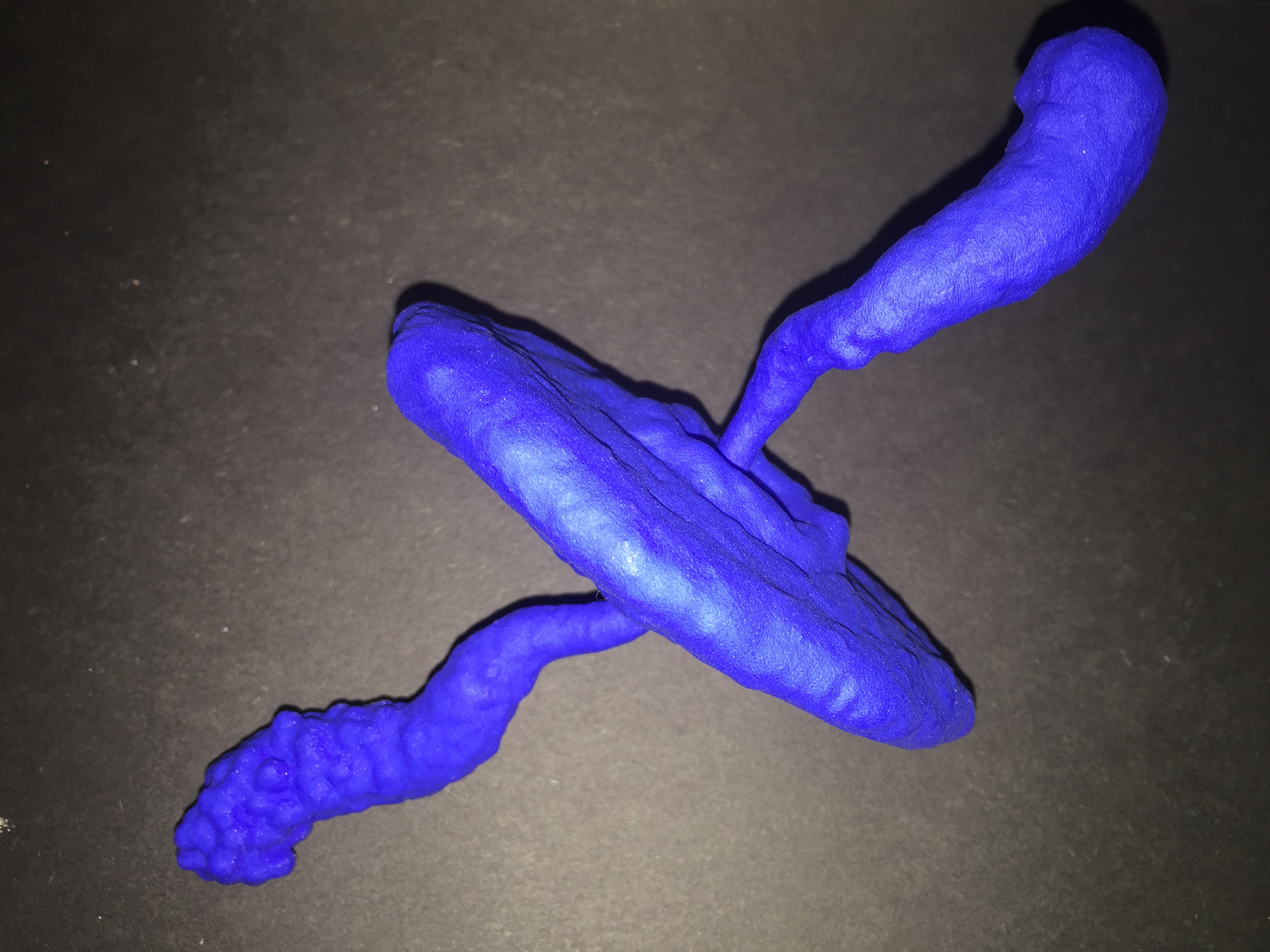

This young star is located about 450 light years from Earth. Material can fall onto a developing star like this, known as a "protostar," from a surrounding disk.
(More information)
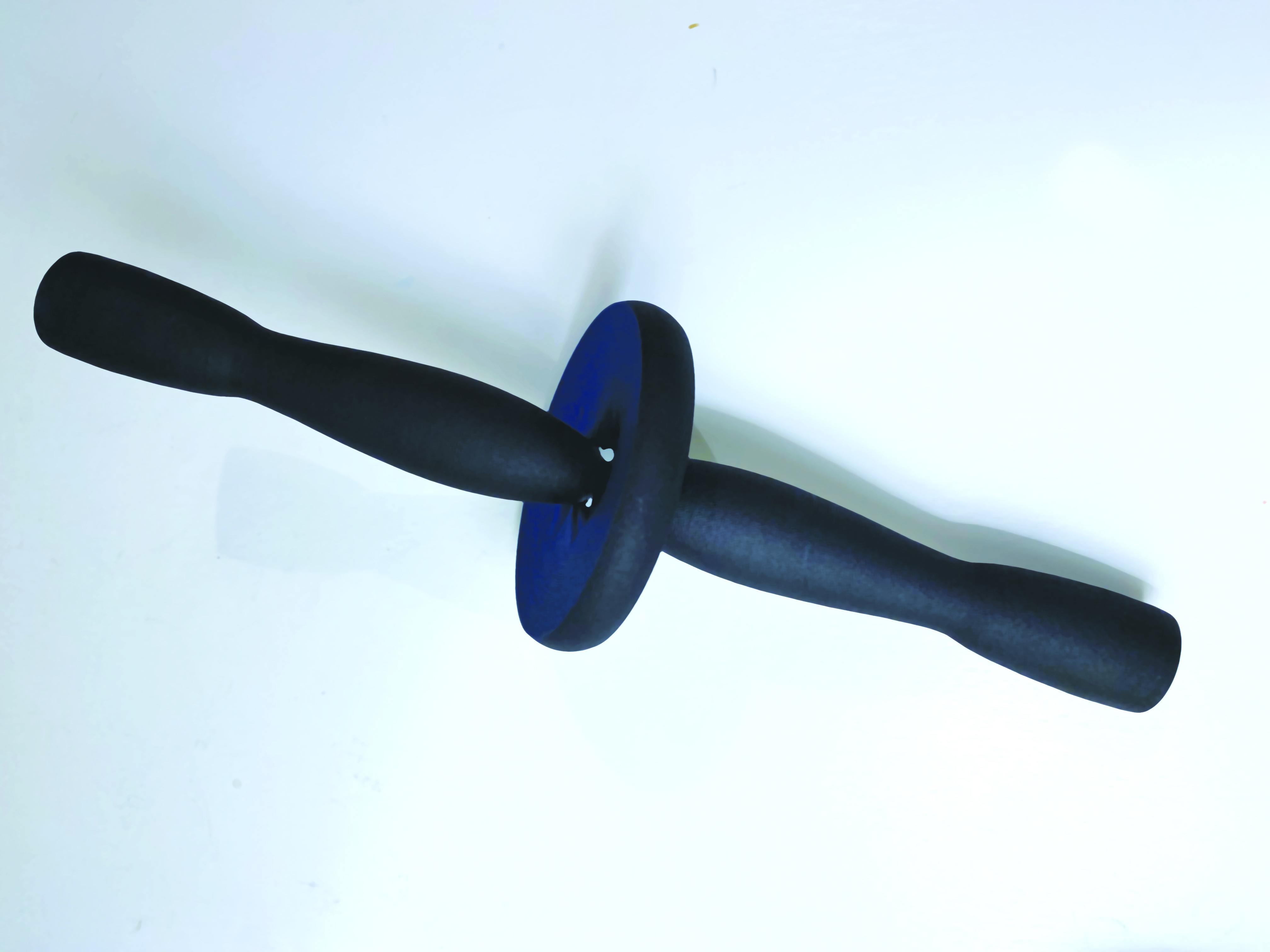

SN (Supernova) 1006 was caused by a white dwarf star that captured mass from a companion star until the white dwarf became unstable and exploded.
(More information)
Download Blast Quarter Globe files
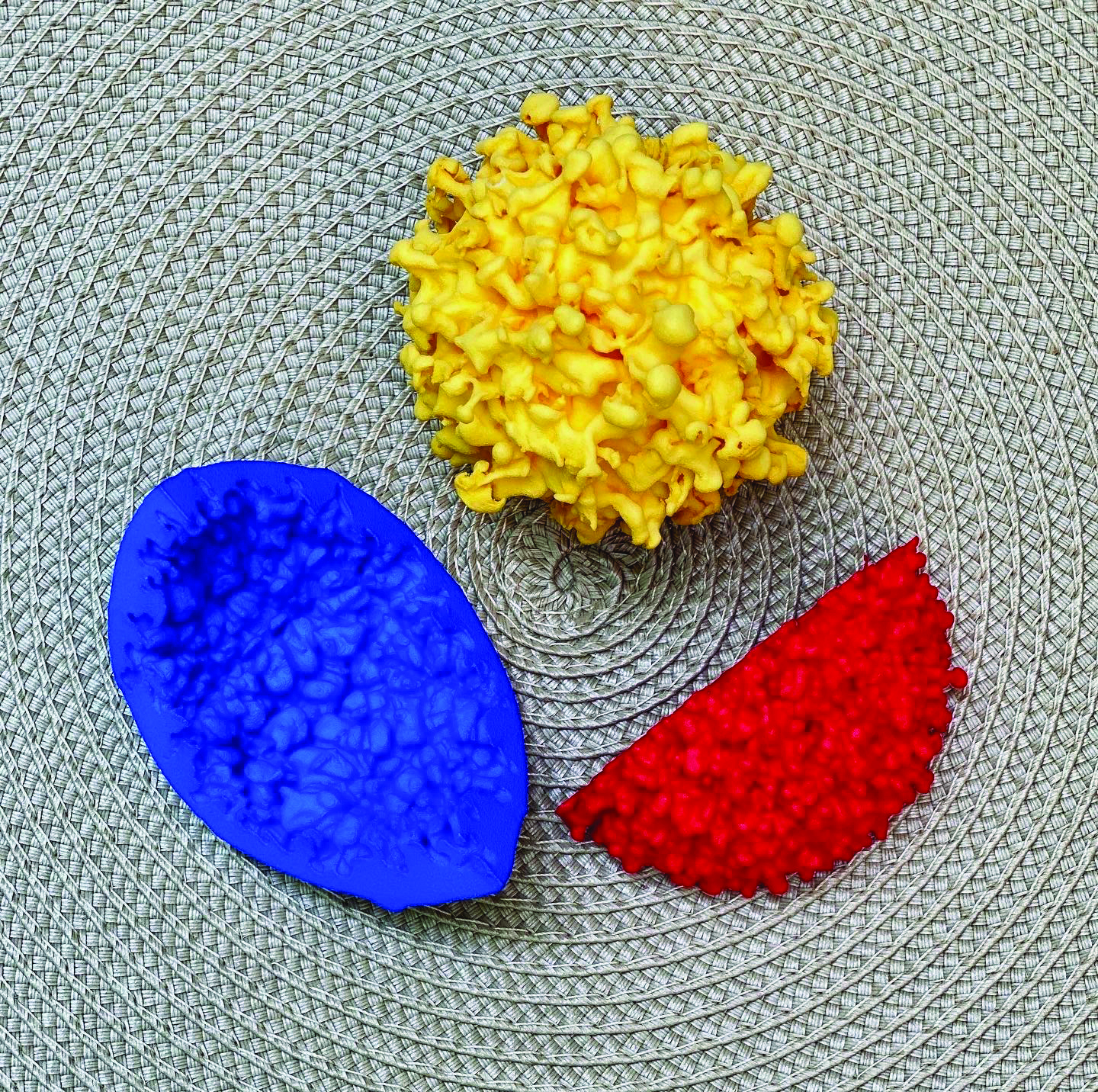
A nova system in which a white dwarf pulls material from its companion star until enough accumulates to trigger a thermonuclear explosion on the white dwarf's surface.
(More information)
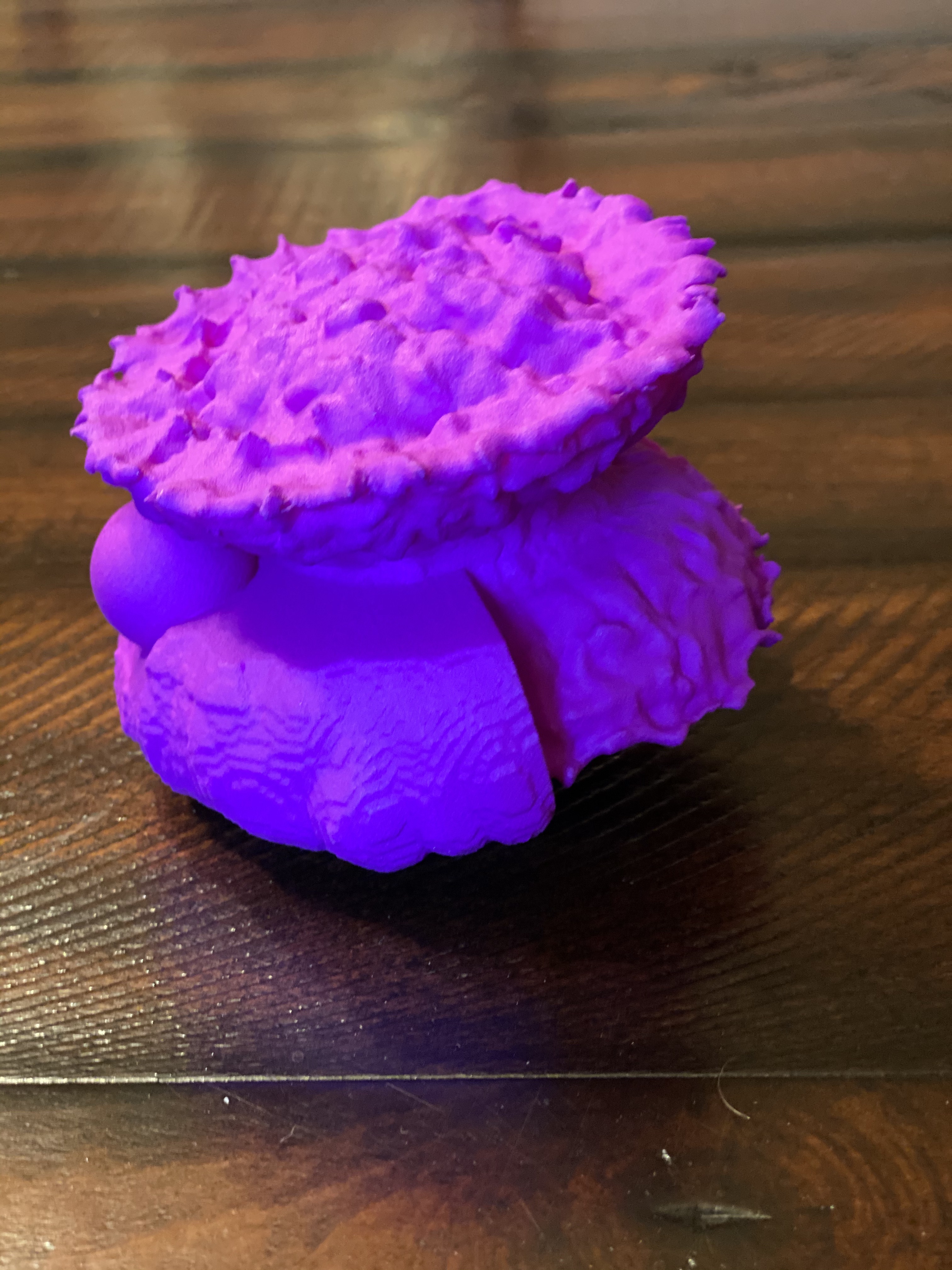

The Jellyfish Nebula, or IC 443, is the remnant of a supernova that occurred about 5,000 light years from Earth.
(More information)

M16, also called the Pillars of Creation, is a nearby star-forming region. The Pillars, which are sometimes called elephant trunks due to their shape, are an example of the column-like shapes that develop in giant clouds of gas and dust that are the birthplaces of new stars. This 3D model depicts details about the orientation of the Pillars in space, mostly that the Pillars actually consist of several distinct pieces on either side of a star cluster. In this model, note that the relative distance between the pillars is not to scale.
This 3D print is based on combined high-resolution spectroscopic data from the European Southern Observatory's (ESO) Very Large Telescope (VLT) with data from the Hubble Space Telescope by McLeod et al., 2015.
(More information)
A star system that contains the most luminous star known in our Galaxy, it radiates energy at a rate that is 5 million times that of the Sun.
(More information)

All photos on the page, credit: NASA/CXC
cxcpub@cfa.harvard.edu
617-496-7941
60 Garden Street,
Cambridge, MA 02138 USA
Art Direction/Design: Kristin DiVona
Web Developer: Khajag Mgrdichian
Chandra X-ray Center, Operated for NASA by the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. This site was developed with funding from NASA under contract NAS8-03060 | Privacy | Accessibility
Additional support from NASA's Universe of Learning (UoL). UoL materials are based upon work supported by NASA under award number NNX16AC65A to the Space
Telescope Science Institute, working in partnership with Caltech/IPAC, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory.

